In Java, we generally create objects using the
There are two methods present in Reflection API which we can use to create objects
Both
In order to use
Below code demonstrates how we can create objects using
Or
It internally use
1. Class.newInstance() can only invoke the no-arg constructor,
Constructor.newInstance() can invoke any constructor, regardless of the number of parameters.
2. Class.newInstance() requires that the constructor should be visible,
Constructor.newInstance() can also invoke private constructors under certain circumstances.
3. Class.newInstance() throws any exception (checked or unchecked) thrown by the constructor,
Constructor.newInstance() always wraps the thrown exception with an InvocationTargetException.
Due to above reasons
You can find complete code on this Github Repository and please feel free to provide your valuable feedback.
new keyword or we use some DI framework e.g. Spring to create an object which internally use Java Reflection API to do so. In this Article, we are going to study the reflective ways to create objects.There are two methods present in Reflection API which we can use to create objects
- Class.newInstance() → Inside java.lang package
- Constructor.newInstance() → Inside java.lang.reflect package
Both
Class.newInstance() and java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance() are known as reflective methods because these two uses reflection API to create the object. Both are not static and we can call earlier one on a class level object while latter one needs constructor level object which we can get by using the class level object.Class.newInstance()
TheClass class is the most popular class in Java after the Object class. However, this class lies in the java.lang package but plays a major role in Reflection API (java.lang.reflect.* package).In order to use
Class.newInstance() we first need to get the class level instance of that class for which we want to create objects. We can do this by two ways one is writing complete name of the class and appending .class to it and another is using Class.forName() method, So in below code Employee.class is similar to (Employee) Class.forName("org.programming.mitra.exercises.Employee")Below code demonstrates how we can create objects using
Class.newInstance()Employee emp = Employee.class.newInstance();Or
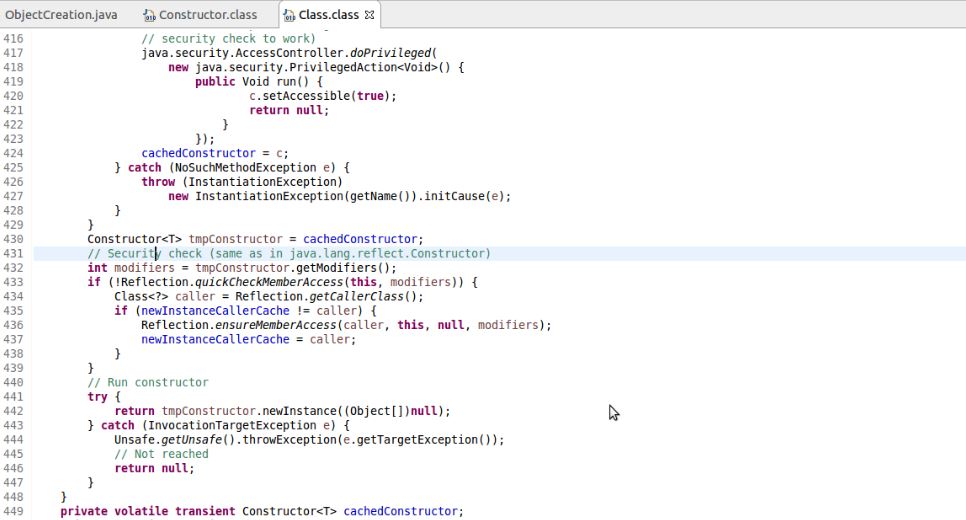
Employee emp = (Employee) Class.forName("org.programming.mitra.exercises.Employee").newInstance();Class.newInstance() internally itself use the Constructor.newInstance() to create the object as we can see in the source code of Class class, notice line no 430 and 442 in below image.
Constructor.newInstance()
In order to useConstructor.newInstance() method we first need to get constructor object for that class and then we can call newInstance() on it to create objects as shown belowConstructor<Employee> constructor = Employee.class.getConstructor();
Employee emp3 = constructor.newInstance();
It internally use
sun.reflect.ConstructorAccessor class to get the object, which is Oracle's private API.Difference between Class.newInstance() and Constructor.newInstance()
By name, both methods look same but there are differences between them which we are as following1. Class.newInstance() can only invoke the no-arg constructor,
Constructor.newInstance() can invoke any constructor, regardless of the number of parameters.
2. Class.newInstance() requires that the constructor should be visible,
Constructor.newInstance() can also invoke private constructors under certain circumstances.
3. Class.newInstance() throws any exception (checked or unchecked) thrown by the constructor,
Constructor.newInstance() always wraps the thrown exception with an InvocationTargetException.
Due to above reasons
Constructor.newInstance() is preferred over Class.newInstance(), that’s why used by various frameworks and APIs like Spring, Guava, Zookeeper, Jackson, Servlet etc.You can find complete code on this Github Repository and please feel free to provide your valuable feedback.
c++ codings by examples
ReplyDeleteSorry Buddy but I do not good knowledge of C++
Deleteexcellent material
ReplyDeleteThanks @Kiran
Delete"Constructor.newInstance() can also invoke private constructors under certain circumstances" what kind of circumstances?
ReplyDeleteThis code will do the trick, it will change the access modifier of the constructor to public
Deletetry {
Constructor constructor = Singleton.class.getDeclaredConstructor();
constructor.setAccessible(true);
singleton = constructor.newInstance();
// Constructor constructor = (Constructor) Class.forName("com.example.bloder.deck.SingletonActivity").getConstructor();
// singleton = constructor.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
exactly..
Delete