This is my third article on Java Cloning series, In previous articles Java Cloning and Types of Cloning (Shallow and Deep) in Details with Example and Java Cloning - Copy Constructor versus Cloning I had discussed Java cloning in detail and explained every concept like what is cloning, how does it work, what are the necessary steps we need to follow to implement cloning, how to use Object.clone(), what is Shallow and Deep cloning, how to achieve cloning using Serialization and Copy constructors and advantages copy of copy constructors over Java cloning.
If you have read those articles you can easily understand why it is good to use Copy constructors over cloning or Object.clone(). In this article, I am going to discuss why copy constructor are not sufficient?
Yes, you are reading it right copy constructors are not sufficient by themselves, copy constructors are not polymorphic because constructors do not get inherited to the child class from the parent class. If we try to refer a child object from parent class reference, we will face problems in cloning it using the copy constructor. To understand it let’s take examples of two classes Mammal and Human where Human extends Mammal, Mammal class have one field type and two constructors, one to create object and one copy constructor to create copy of an object
And Human class which extends Mammal class, have one name field, one normal constructor and one copy constructor to create copy
Now let’s create objects for both classes
Now if we want to create clone for mammal or human, we can simply do it by calling their respective copy constructor
We will get no error in doing this and both objects will be cloned successfully, as we can see below tests
But what if we try to refer object of Human from reference of Mammal
In order to clone mammalHuman, we can not use constructor Human, It will give us compilation error because type mammalHuman is Mammal and constructor of Human class accept Human.
And if we try clone mammalHuman using copy constructor of Mammal, we will get the object of Mammal instead of Human but mammalHuman holds object of Human
So both mammalHuman and clonedMammalHuman are not the same objects as you see in the output below code
Output:
As we can see copy constructors suffer from inheritance problems and they are not polymorphic as well. So how can we solve this problem, Well there various solutions like creating static Factory methods or creating some generic class which will do this for us and the list will go on.
But there is a very easy solution which will require copy constructors and will be polymorphic as well.We can solve this problem using defensive copy methods, a method which we are going to include in our classes and call copy constructor from it and again override it the child class and call its copy constructor from it.
Defensive copy methods will also give us advantage of dependency injection, we can inject dependency instead of making our code tightly coupled we can make it loosely coupled, we can even create an interface which will define our defensive copy method and then implement it in our class and override that method.
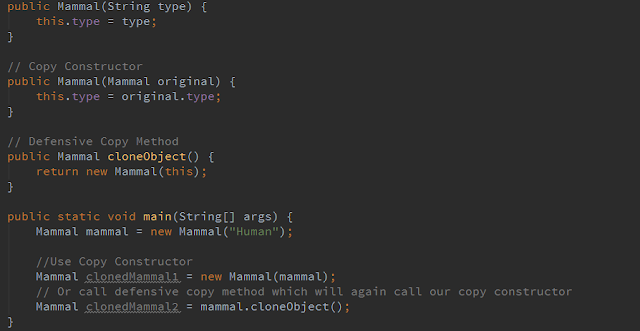
So in Mammal class we will create a no-argument method cloneObject however, we are free to name this method anything like clone or copy or copyInstance
And we can override same in “Human” class
Now to clone mammalHuman we can simply say
And for last two sys out we will get below output which is our expected behavior.
As we can see apart from getting the advantage of polymorphism this option also gives us freedom from passing any argument.
You can found complete code in CopyConstructorExample Java file on Github and please feel free to give your valuable feedback.
If you have read those articles you can easily understand why it is good to use Copy constructors over cloning or Object.clone(). In this article, I am going to discuss why copy constructor are not sufficient?

Yes, you are reading it right copy constructors are not sufficient by themselves, copy constructors are not polymorphic because constructors do not get inherited to the child class from the parent class. If we try to refer a child object from parent class reference, we will face problems in cloning it using the copy constructor. To understand it let’s take examples of two classes Mammal and Human where Human extends Mammal, Mammal class have one field type and two constructors, one to create object and one copy constructor to create copy of an object
class Mammal {
protected String type;
public Mammal(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Mammal(Mammal original) {
this.type = original.type;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Mammal mammal = (Mammal) o;
if (!type.equals(mammal.type)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return type.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Mammal{" + "type='" + type + "'}";
}
}
And Human class which extends Mammal class, have one name field, one normal constructor and one copy constructor to create copy
class Human extends Mammal {
protected String name;
public Human(String type, String name) {
super(type);
this.name = name;
}
public Human(Human original) {
super(original.type);
this.name = original.name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
if (!super.equals(o)) return false;
Human human = (Human) o;
if (!type.equals(human.type)) return false;
if (!name.equals(human.name)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = super.hashCode();
result = 31 * result + name.hashCode();
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Human{" + "type='" + type + "', name='" + name + "'}";
}
}
Here in both copy constructors we are doing deep cloning.
Now let’s create objects for both classes
Mammal mammal = new Mammal("Human");
Human human = new Human("Human", "Naresh");
Now if we want to create clone for mammal or human, we can simply do it by calling their respective copy constructor
Mammal clonedMammal = new Mammal(mammal);
Human clonedHuman = new Human(human);
We will get no error in doing this and both objects will be cloned successfully, as we can see below tests
System.out.println(mammal == clonedMammal); // false
System.out.println(mammal.equals(clonedMammal)); // true
System.out.println(human == clonedHuman); // false
System.out.println(human.equals(clonedHuman)); // true
But what if we try to refer object of Human from reference of Mammal
Mammal mammalHuman = new Human("Human", "Mahesh");
In order to clone mammalHuman, we can not use constructor Human, It will give us compilation error because type mammalHuman is Mammal and constructor of Human class accept Human.
Mammal clonedMammalHuman = new Human(mammalHuman); // compilation error
And if we try clone mammalHuman using copy constructor of Mammal, we will get the object of Mammal instead of Human but mammalHuman holds object of Human
Mammal clonedMammalHuman = new Mammal(mammalHuman);
So both mammalHuman and clonedMammalHuman are not the same objects as you see in the output below code
System.out.println("Object " + mammalHuman + " and copied object " + clonedMammalHuman + " are == : " + (mammalHuman == clonedMammalHuman));
System.out.println("Object " + mammalHuman + " and copied object " + clonedMammalHuman + " are equal : " + (mammalHuman.equals(clonedMammalHuman)) + "\n");
Output:
Object Human{type='Human', name='Mahesh'} and copied object Mammal{type='Human'} are == : false
Object Human{type='Human', name='Mahesh'} and copied object Mammal{type='Human'} are equal : false
As we can see copy constructors suffer from inheritance problems and they are not polymorphic as well. So how can we solve this problem, Well there various solutions like creating static Factory methods or creating some generic class which will do this for us and the list will go on.
But there is a very easy solution which will require copy constructors and will be polymorphic as well.We can solve this problem using defensive copy methods, a method which we are going to include in our classes and call copy constructor from it and again override it the child class and call its copy constructor from it.
Defensive copy methods will also give us advantage of dependency injection, we can inject dependency instead of making our code tightly coupled we can make it loosely coupled, we can even create an interface which will define our defensive copy method and then implement it in our class and override that method.
So in Mammal class we will create a no-argument method cloneObject however, we are free to name this method anything like clone or copy or copyInstance
public Mammal cloneObject() {
return new Mammal(this);
}
And we can override same in “Human” class
@Override
public Human cloneObject() {
return new Human(this);
}
Now to clone mammalHuman we can simply say
Mammal clonedMammalHuman = mammalHuman.clone();
And for last two sys out we will get below output which is our expected behavior.
Object Human{type='Human', name='Mahesh'} and copied object Human{type='Human', name='Mahesh'} are == : false
Object Human{type='Human', name='Mahesh'} and copied object Human{type='Human', name='Mahesh'} are equal : true
As we can see apart from getting the advantage of polymorphism this option also gives us freedom from passing any argument.
You can found complete code in CopyConstructorExample Java file on Github and please feel free to give your valuable feedback.
Nice article
ReplyDeleteThanks
Deletejava swing
ReplyDelete